Book Value Formula How to Calculate Book Value of a Company?
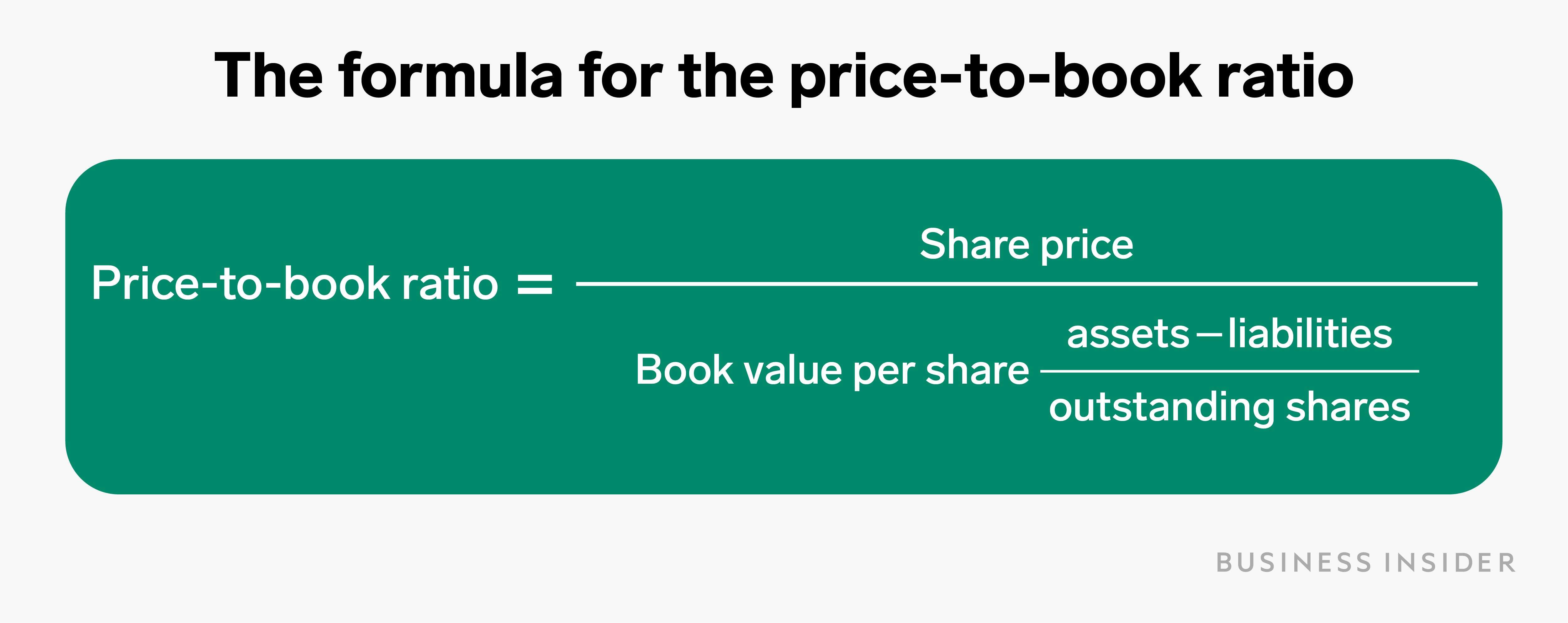
Manufacturing companies offer a good example of how depreciation can affect book value. These companies have to pay huge amounts of money for their equipment, but the resale value for equipment usually goes down faster than a company is required to depreciate it under accounting rules. Making Calculations Practical Now it’s time to use the calculation for something.
What Does Book Value Per Share (BVPS) Tell Investors?
For instance, banks or high-tech software companies often have very little tangible assets relative to their intellectual property and human capital (labor force). These intangibles would not always be factored in to a book value calculation. A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS. Or, it could use its earnings to reduce liabilities, which would also increase its common equity and BVPS.
Example of BVPS
Book value is the value of a company’s assets after netting out its liabilities. It approximates the total value shareholders would receive gary cogley if the company were liquidated. There are a number of other factors that you need to take into account when considering an investment.
How to Interpret BVPS?
Undervalued stock that is trading well below its book value can be an attractive option for some investors. It depends on a number of factors, such as the company’s financial statements, competitive landscape, and management team. Even if a company has a high book value per share, there’s no guarantee that it will be a successful investment. This is why it’s so important to do a lot of research before making any investment decisions. BVPS is typically calculated and published periodically, such as quarterly or annually. This infrequency means that BVPS may not always reflect the most up-to-date value of a company’s assets and liabilities.
- For example, the company’s financial statements, competitive landscape, and management team.
- Rather than buying more of its own stock, a company can use profits to accumulate additional assets or reduce its current liabilities.
- However, for sectors like technology and pharmaceuticals, where intellectual property and ongoing research and development are crucial, BVPS can be misleading.
How to Calculate BVPS?
The first thing one might do is compare the price/BVPS number to the historic trend. In this case, the company’s price/BVPS multiple seems to have been sliding for several years. In this case, the stock seems to trade at a multiple that is roughly in line with its peers. If the company is going through a period of cyclical losses, it may not have positive trailing earnings or operating cash flows. Therefore, an alternative to the P/E approach may be used to assess the current value of the stock. This is especially applicable when the analyst has low visibility of the company’s future earnings prospects.
Is BVPS relevant for all types of companies?

By leveraging useful and insightful formulas such as a company’s Book Value Per Share, investors can determine a company’s value relative to its current market price. Measuring the Value of a ClaimA good measure of the value of a stockholder’s residual claim at any given point in time is the book value of equity per share (BVPS). Book value is the accounting value of the company’s assets less all claims senior to common equity (such as the company’s liabilities). In the example from a moment ago, a company has $1,000,000 in equity and 1,000,000 shares outstanding.
An asset’s book value is calculated by subtracting depreciation from the purchase value of an asset. Depreciation is generally an estimate, and there are various methods for calculating depreciation. Critics of book value are quick to point out that finding genuine book value plays has become difficult in the heavily-analyzed U.S. stock market. Oddly enough, this has been a constant refrain heard since the 1950s, yet value investors continue to find book value plays. Failing bankruptcy, other investors would ideally see that the book value was worth more than the stock and also buy in, pushing the price up to match the book value. For example, if a company has a total asset balance of $40mm and liabilities of $25mm, then the book value of equity (BVE) is $15mm.
Book value per share relates to shareholders’ equity divided by the number of common shares. Earnings per share would be the net income that common shareholders would receive per share (company’s net profits divided by outstanding common shares). BVPS relies on the historical costs of assets rather than their current market values. This approach can lead to significant discrepancies between the book value and the actual market value of a company’s assets. Over time, the historical cost basis may not reflect the true worth of assets due to inflation, depreciation, and changes in market conditions, leading to potential misvaluation of the company’s stock.

